Most people understand nonverbal communication just like they understand their native language. On the other hand, intuitive comprehension is not enough to help online tutors gain a deeper knowledge of the efficiency and effectiveness of their teaching and learning process. This is why acquiring a deeper knowledge of, as well as consciously searching for nonverbal cues, is vital for the improvement of the tutor’s performance in virtual classroom. This enables the tutor to change strategies, if needed, as well as to diversify the content of the session and to be more efficient while instructing the students.
Nonverbal communication – what is it?
The term nonverbal communication is broader than the term body language even though they are often used synonymously. Nonverbal communication consists of all of the pieces of information that are transmitted from a communicator to a receiver using methods other than verbal ones. It can be described as a natural, unconscious language that manifests true feelings and intentions. Nonverbal communication is the sum of all wordless cues that people send and receive in the process of communication, as well as the sum of all nonverbal behaviors that convey meaning. It constitutes about 93 percent of all communication.
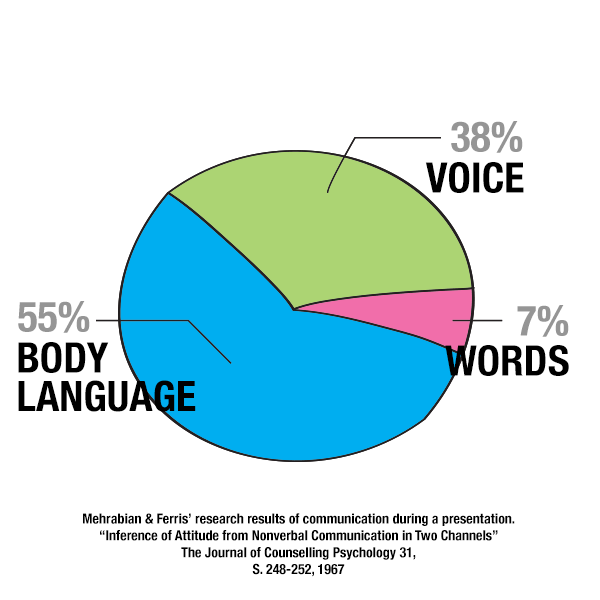
The relationship between verbal and nonverbal communication is very important. When words do not match what the body is “saying” people may feel confused and prefer to believe what the nonverbal signs are hinting at.
“The important thing to remember when looking at such nonverbal behaviors is to consider the actions in groups. What a person actually says along with his or her expressions, appearance, and tone of voice might tell you a great deal about what that person is really trying to say.”1
Aspects of nonverbal communication
Nonverbal communication includes typical body language gestures, facial expressions, eye contact, posture, and physical appearance, but also personal space, proxemics, paralinguistics, and haptics. Each of these provide different information if one knows what to look for.
1. Facial expressions
People’s faces differ tremendously due to gender, ethnicity, race, etc. But they do have common expressions. The expressions that people all around the world share and can easily recognize are happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, fear, and disgust. The way a face looks can often say much more than a thousand words can, making facial expressions one of the most important and effective nonverbal cues.
2. Gestures
In their daily lives people often wave, point, or use their hands while speaking. Gestures are deliberate movements and signals that enrich what is verbally expressed. In order to avoid misunderstandings and problems, people should bear in mind that the use of gestures varies significantly across cultures and religions.
3. Paralinguistics – the power of the voice
Other than the verbal communication that refers to what is said, there is also the nonverbal aspect of how it is said. Paralinguistics is what allows people to “read” a voice using characteristics like tone, loudness, inflection, pace, and pitch. A good illustration is sarcasm, which can only be detected or defined by the deliberate impression that is has left on the addressee.
4. Body language and posture
Body language is, as already stated, a part of nonverbal communication. The movements of the body and the posture of a person convey a very strong message. People easily identify “closed” or defensive postures such as arm- or leg-crossing.
5. Proxemics – personal space
Proxemics is what is commonly known as personal space. This is the distance from others that people need to feel safe and comfortable in their surrounding environment. Like gestures, this part of nonverbal communication is defined by various factors like social norms, culture, type of situation, personal traits, and level of intimacy. The amount of space can convey different signals – intimacy and affection, aggression, or dominance.
6. Eye contact
It is said that the eyes are the windows to the soul. Looking, staring, and even blinking are important nonverbal cues. A gaze can express a variety of feelings such as interest, affection, hostility, or attraction. The sense of vision is dominant for most people and it determines the essential role of eye contact in maintaining a conversation – both as an expression of participation and as a source of knowledge about the addressee’s interest and response.
7. Touch
Haptics is communication through touch. Touch can convey affection, familiarity, sympathy, but also status and power. How and to what extent touch is used is primarily defined by gender and cultural differences. It is generally believed that a woman’s touch refers to nurturing, motherhood, caring, and safety, whereas a strong manly touch is a sign of control and dominance.
8. Appearance – how we look
As already discussed, people are visual creatures, i.e., they perceive their surroundings predominantly by the way it looks. It is not surprising that things such as clothes, colors, hair, accessories, etc. constitute an important means of nonverbal communication. Nowadays researchers have even developed a study on how different colors evoke specific moods and also on how one’s look can determine the salary that an employer is willing to pay.
